About Cholesterol

Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is currently a leading cause of death in Malaysia and many other developed countries. The culprit? No surprises here–high cholesterol! Prevalence of common cardiovascular risk factors among those over 18 years old are increasing in trend, and it is the same at both rural and urban areas.
Malaysians mean age of having Acute Coronary Syndrome is at 58.5 years (lower than our neighbouring countries), with 6.6% were < 40 years old.1
So what is cholesterol exactly?
Cholesterol is a fatty substance in our blood, produced naturally in the liver. It is a waxy substance that circulates through the bloodstream and is used to create cells, hormones, and vitamin D. Due to the nature of its waxy texture, cholesterol does not dissolve in the blood. It bonds to 'packages' known as lipoproteins that transport cholesterol through the bloodstream. Too much cholesterol in the blood can lead to heart and blood circulation diseases, which is why it is important to follow a healthy diet and exercise regularly to keep your heart happy.
Types of cholesterol
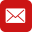
There are 2 main types of cholesterol:
-
HDL cholesterol helps to remove LDL from the blood vessels through blood stream into the liver. The liver then breaks it down and removes bad cholesterol it from the body. Higher levels of HDL are better, as it is the protector against LDL (low-density lipoprotein). HDL does not eliminate LDL as only a third to a quarter of blood cholesterol is carried by HDL.Through the process of HDL, it could help lower the risk of heart disease or stroke. It is important to follow a healthy diet and minimisefoods that are high in LDL, which could increase your risk of heart disease.
-
Excessive LDL cholesterol builds up on the walls of your blood vessels, called “plaque.” As plaque builds up over time, the insides of the vessels narrow, clogging the path for blood flow to and from your heart and other organs, potentially causing a heart attack. These diseases are not only associated with older people, as the percentage of youths suffering from heart disease is increasing.An unhealthy diet and lack of exercise play a huge role in the build-up of LDL, which can be avoided. Following a healthy diet and doing regular exercise can better your chances of lowering your cholesterol
What are the risk factors?
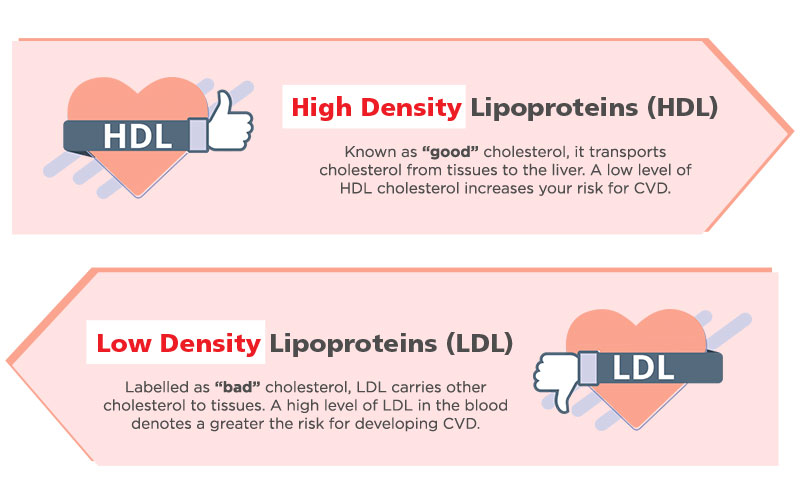
When it comes to what causes high cholesterol, there are 2 major groups of factors – factors that can be changed and cannot be changed.
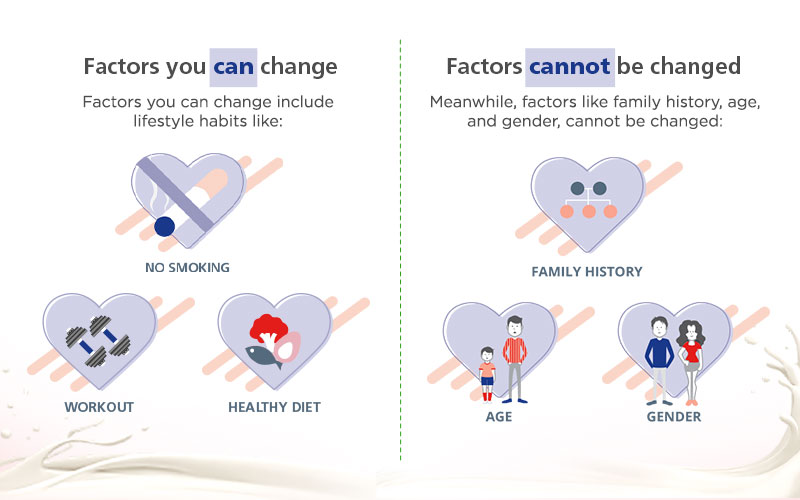
Factors you can change include lifestyle habits like physical inactivity, smoking, and unhealthy diet.Take central obesity, for instance: it is caused by poor diet and lack of exercise. Regular workouts and a higher intake of fruits and vegetables can gradually help reduce the risk for CVD.
Meanwhile, factors like family history, age, and gender, cannot be changed.
GENDER: The incidence of CVD increases with age and men are 3–4 times more likely to be affected compared to women in middle decades, or almost twice among elderlies.
AGE: Presence of premature coronary disease in first degree male relatives with age < 55 years or female relatives < 65 years.2
LIFESTYLE: The incidence and mortality of heart disease is 2-3 times as high in cigarette smokers compared to non-smokers.3
In Asians, a waist circumference of > 90 cm in men and > 80 cm in women has been found to be associated with increased heart disease risk.4
Science has shown that physical inactivity is associated with increased mortality and heart disease.5
References:
Acute Coronary Syndrome (NCVD-ACS) 2011-2013 Study
Conditions: Cardiovascular Disease NHS, UK
https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/risk-factors/high-cholesterol